Python Keywords and Identifiers
Keywords are reserved word in Python programming language that cannot be used for naming variables, constants or function names in while writing Python programs. Identifiers are the names given to the variables, constants, functions, classes etc. In this tutorial, we will learn more about what are the keywords and some rules for naming identifiers.
Contents
What are Keywords for Python?
Keywords in python represent reserved words that cannot be used as identifiers. Following are the list of keywords in Python.
| and | exec | not |
| assert | finally | or |
| break | for | pass |
| class | from | |
| continue | global | raise |
| def | if | return |
| del | import | try |
| elif | in | while |
| else | is | with |
| except | lambda | yield |
Let us go through some keywords and their use:-
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| and | A logical operator that produces true if all values are right |
| as | To create an alias in Python |
| assert | For debugging purpose |
| break | To break out of a loop |
| class | Used to create a class in Python |
| continue | To continue to the next iteration of a loop |
| def | The definition of a function starts with def keyword |
| del | To delete an object |
| elif | Used in conditional statements, same as else if |
| else | Conditional statement used with if statement |
| except | Used with exceptions, what to do when an exception occurs |
| False | Boolean value, the result of comparison operations |
| finally | Used with exceptions, a block of code that will be executed no matter if there is an exception or not |
| for | To create a for loop |
| from | To import specific parts of a module |
| global | To declare a global variable |
| if | To make a conditional statement |
| import | To import a module |
| in | To check if a value is present in a list, tuple, etc. |
| is | To test if two variables are equal |
| lambda | To create an anonymous function |
| None | Represents a null value |
| nonlocal | To declare a non-local variable |
| not | A logical operator to check if it is not |
| or | A logical operator produces true if all any one of the value is right |
| pass | A null statement, a statement that will do nothing |
| raise | To raise an exception |
| return | To exit a function and return a value |
| True | Boolean value, the result of comparison operations |
| try | To make a try…except statement |
| while | To create a while loop |
| with | Used to simplify exception handling |
| yield | To end a function, returns a generator |
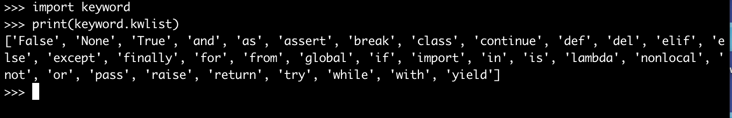
How to see the list of keywords available in Python?
To see the list of available keywords, you can use the command as shown below:-
import keyword print(keyword.kwlist)
What is an identifier in Python?
In Python, an identifier is a name used to identify a variable, function, class, module or other objects. Identifier begins with a letter a to z or A to Z or an underscore (_) trailed by zero or more letters, underscores, and digits (0 to 9). An identifier is a name given to entities like class, functions, variables etc. in Python. It helps to differentiate one entity from another.
What are the naming conventions for Python identifiers?
- Identifier begins with a letter a to z or A to Z or an underscore (_) trailed by zero or more letters, underscores, and digits (0 to 9)
- We cannot use keywords as an identifier name
- An identifier cannot start with a digit. 5variable is an invalid identifier, however, digits can be added after the variable name.
- The use of special symbols like !, @, #, $, % etc. is forbidden in an identifier.
- An identifier can be of any length, however, it is always good to make it shorter to make it more readable.
- Class names start with an uppercase letter. All other identifiers start with a lowercase letter.
- Starting an identifier with a single leading underscore indicates that the identifier is private.
- Starting an identifier with two leading underscores indicates a strongly private identifier.
- If the identifier also ends with two trailing underscores, the identifier is a language-defined special name.
Python is a case-sensitive language. This means Variable and variable are not the same. Make sure you name them carefully.
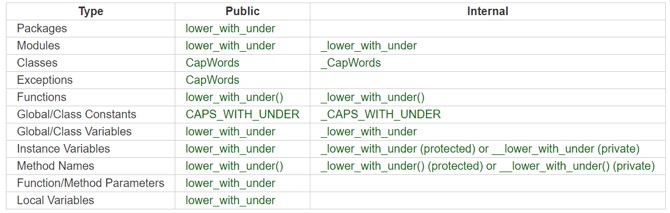
Guidelines derived from Guido’s Recommendations
Here are the guidelines that is derived from Guido that helps you better obtain uniform programming guidelines for your python projects.
What is Python Coding Style?
Python coding style is defined by PEP-8 style which stands for Python Enhancement Proposal that provides a proper technical documentation and rules that is made standard in the Python community. Here are some of the guidelines that is provided in PEP-8.
- Use 4 spaces per indentation and no tabs.
- Do not mix tabs and spaces. Tabs create confusion and it is recommended to use only spaces.
- Maximum line length : 79 characters which help users with a small display.
- Use blank lines to separate top-level function and class definitions and single blank line to separate
- methods definitions inside a class and larger blocks of code inside functions.
- When possible, put inline comments (should be complete sentences).
- Use spaces around expressions and statements.
Do visit https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/ for PEP 8 — Style Guide for Python Code.