Implementation of fixed precision numbers in Flutter
The Fixed package allows you to store and perform maths on decimal numbers with a fixed scale (fixed no. of decimal places).
All amounts are store using the Decimal package to allow precision maths to be performed.
The Fixed package allows you to have explicit control over the no. of decimals (the scale) that are stored.
The key difference between the Decimal and Fixed packages:
- Fixed uses a fixed scale (no. of decimal places)
- Fixed provides a builtin formatter
Fixed.format(pattern) - Fixed includes a convenience method
Fixed.formatIntl(locale)which formats the number with the provided locale or the default locale if not provided. - Most Fixed constructors take minorUnits and a scale (100 scale: 2 == 1.00)
Storing fixed amounts
If you need to store a fixed value into a db or other store we recommend that you store the value as to discrete numbers; minorUnits and scale. Storing the value using this technique guarentees no precision loss when storing, transmitting or retrieving Fixed decimal values.
Constructors
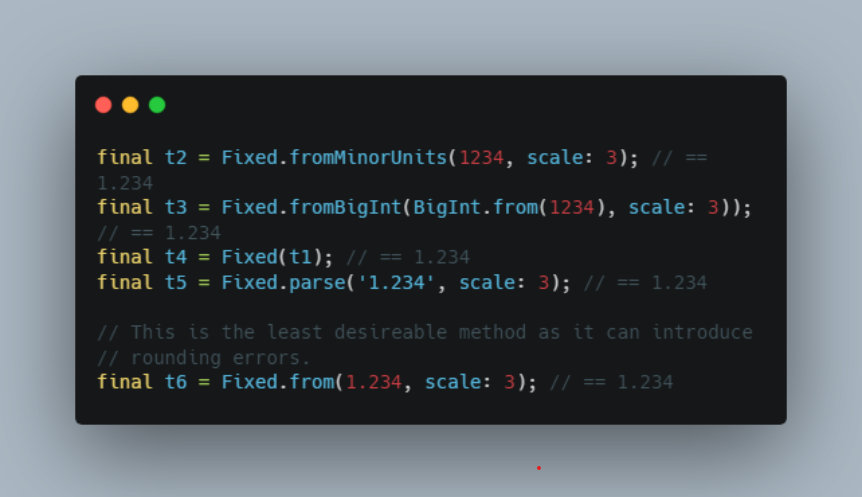
There are multiple ways you can create a Fixed object
final t2 = Fixed.fromMinorUnits(1234, scale: 3); // == 1.234
final t3 = Fixed.fromBigInt(BigInt.from(1234), scale: 3)); // == 1.234
final t4 = Fixed(t1); // == 1.234
final t5 = Fixed.parse('1.234', scale: 3); // == 1.234
final t6 = Fixed.fromDecimal(Decimal.fromInt(1), scale: 2); // == 1.00
// This is the least desireable method as it can introduce
// rounding errors.
final t7 = Fixed.from(1.234, scale: 3); // == 1.234Scale
The Fixed package stores no.s with a fixed scale (number of decimal places).
If you attempt an operation on two Fixed values with different scale the result will mostly be the larger of the two scales.
You can change the scale of a number by creating a new Fixed object with the required scale.
final t7 = Fixed.from(1.234, scale: 3); // == 1.234 /// reduce the scale final t8 = Fixed(t7, scale: 2); // == 1.23 /// increase the scale final t8 = Fixed(t7, scale: 5); // == 1.23000
Parsing
You can parse numbers from strings:
var t1 = Fixed.parse('1.234', scale: 2);
expect(t1.minorUnits.toInt(), equals(1234));
expect(t1.scale, equals(2));
var t1 = Fixed.parse('1,000,000.234', scale: 2);
expect(t1.minorUnits.toInt(), equals(1000000.23));
expect(t1.scale, equals(2));
/// for countries that use . for group separators
var t1 = Fixed.parse('1.000.000,234', scale: 2, invertSeparators);
expect(t1.minorUnits.toInt(), equals(1000000.23));
expect(t1.scale, equals(2));Formating
You can also format numbers to strings
var t1 = Fixed.fromMinorUnits(1234, scale: 3);
expect(t3.toString(), equals('1.234'));
expect(t3.format('00.###0'), equals('00.12340'));
expect(t3.format('00.###0', invertSeparator: true), equals('00,12340'));
var euFormat = Fixed.parse('1.000.000,23', invertSeparators: true, scale: 2)
// Format using a locale
expect(euFormat.formatIntl('en-AUS'), equals('1,000,000.23'));
// Format using default locale
expect(euFormat.formatIntl(), equals('1,000,000.23'));Performing maths
When performing most mathematical operations the larger scale of the two operands is used.
For multiplication the resulting scale is the sum of the two scales e.g.
0.01 * 0.02 = 0.0002
If you need to change the scale of a number just create a new Fixed object with the required scale
Fixed(Fixed.from(5, scale: 2), scale: 10);
Operators
Fixed provides mathematical operations:
final t1 = Fixed.parse('1.23'); // = 1.23
final t2 = Fixed.fromMinorUnits(100, scale: 2); // = 1.00
final t3 = t1 + t2; // == 2.23
final t4 = t2 - t1; // == 0.23
final t5 = t1 * t2; // == 1.23;
final t6 = t1 / t2; // == 1.23
final t7 = -t1; // == -1.23
Comparision
final t1 = Fixed.from(1.23); final t2 = Fixed.fromMinorUnits(123, scale: 2); final t3 = Fixed.fromBigInt(BigInt.from(1234), scale: 3)); expect(t1 == t2, isTrue); expect(t1 < t3, isTrue); expect(t1 <= t3, isTrue); expect(t1 > t3, isFalse); expect(t1 >= t3, isFalse); expect(t1 != t3, isTrue); expect(-t1, equals(Fixed.fromMinorUnits(-123, scale: 2))); expect(t1.isPositive, isTrue); expect(t1.isNegative, isFalse); expect(t1.isZero, isTrue); expect(t1.compareTo(t2) , isTrue);
GitHub
Source Code: Fixed Precision Numbers in Flutter.