Binary Addition and Subtraction using C Program
Contents
Introduction
The C programming language is a procedural programming language. Between 1969 and 1973, Dennis Ritchie worked on the project. It was created primarily as a system programming language for developing operating systems. Low-level memory access, a small collection of keywords, and a clean style are all qualities that make C language excellent for system programming, such as operating system or compiler development.
Why Learn C Programming Language?
Because it mixes the characteristics of high-level languages with the functionalism of assembly language, C is often referred to as a middle-level computer language. The manipulation of bits, bytes, and addresses in C gives the programmer more control over how the program will behave and more direct access to the underlying hardware mechanisms.
Working programmers influenced, influenced, and field-tested C. As a result, C provides the programmer with exactly what he or she want. C++ is a more advanced version of the C programming language. C++ incorporates all of the features of C, as well as support for object-oriented programming (OOP). Furthermore, C++ includes numerous enhancements and features that make it a “better C,” regardless of whether or not it is used for object-oriented programming.
Binary Addition and Subtraction
In binary numerals, the numbers ‘0’ and ‘1’ are utilized. This number system can be used to represent, store, and transmit data and information electronically. It is simple and natural to divide things into two states under electrical technology, whether there is power supply or not.
Binary addition/subtraction is comparable to conventional (everyday life) addition/subtraction, except it only uses two digits: 0 and 1, which are binary digits, hence it’s called binary addition/subtraction.
The best way to learn is to do. Hence, what better way to learn C programming language (if you know the basics) than to code your first mini project. In this tutorial we are going to build a binary adder and subtractor using c programming language. Keep in mind this is a mini project for absolute beginners and intermediate programmers as well.
Example 1: Binary Addition
In binary addition. Unlike the conventional way, the following are the rules:
0 + 0 = 0
0 + 1 = 1
1 + 0 = 1
1 + 1 = 0 (1 is taken as carry / 1 carries out)
Now add 85 and 181
(85)10 = 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
(181)10 = 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1
_____________________________________
= 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0
= (266)10Example 2: Binary Subtraction
In binary subtraction. Unlike the conventional way, the following are the rules:
0 - 0 = 0
1 - 0 = 1
0 - 1 = 1 (1 is taken as borrow / 1 borrows out)
1 - 1 = 0
Now sub 7 from 45
(45)10 = 1 0 1 1 0 1
(7)10 = 0 0 0 1 1 1
____________________________
= 1 0 0 1 1 0
= (38)10Source Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <conio.h>
// function for Binary Addition
int binAddition(int a,int b)
{
// initiallizing our carry
int c;
while (b != 0) {
// find carry and shift it left
c = (a & b) << 1;
// find the sum
a=a^b;
b=c;
}
return a;
}
// function for Binary Subtraction
int binSubtracton(int a, int b)
{
int carry;
// get 2's compliment of b and add in a
b = binAddition(~b, 1);
while (b != 0) {
// find carry and shift it left
carry = (a & b) << 1;
//find the sum
a = a ^ b;
b = carry;
}
return a;
}
int main()
{
int number1,number2, binAdd, binSub;
printf("Input first integer value: ");
scanf("%d",&number1);
printf("Input second integer value: ");
scanf("%d",&number2);
binAdd = binAddition(number1,number2);
binSub = binSubtracton(number1,number2);
printf("Binary Addition: %d\n",binAdd);
printf("Binary Subtraction: %d\n",binSub);
return 0;
}Output
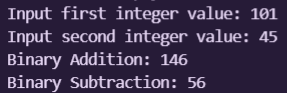
The output for the given code above are:
- Output Screenshot 1 :
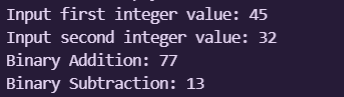
- Output Screenshot 2 :
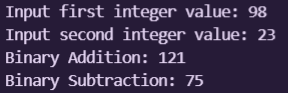
- Output Screenshot 3 :